This article introduces methods to debug programs in Excel VBA and improve development efficiency. We’ll examine breakpoint creation and usage in Excel VBA, Run to cursor, variable checking and program expression monitoring, and trick methods to virtually use REPL (interactive execution).
Enable Development Mode and VBA in Excel
First, confirm that Developer mode is enabled to open the VBA editor in Excel.
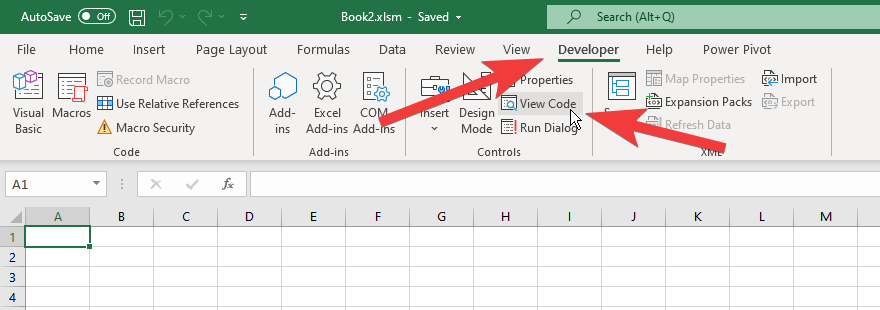
If there’s no Developer tab, enable development mode.
Click Options from the Excel menu screen to open settings.
In the settings options screen, proceed with Customize Ribbon > Developer > OK
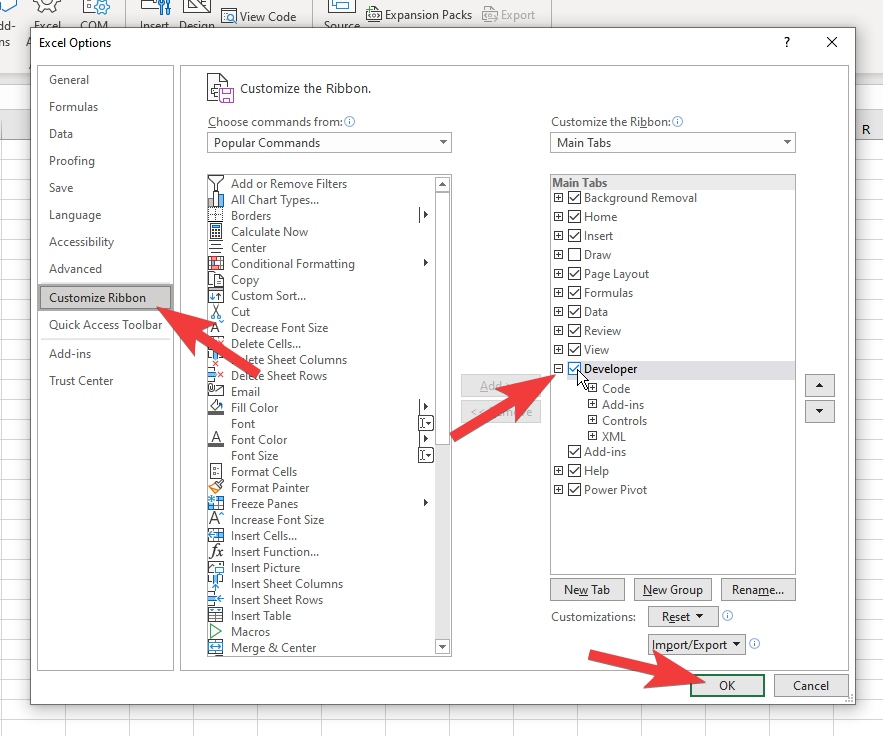
At this point, the Developer tab should be added as shown in the image above.
Click view code on the Developer tab to open the VBA editor.
Debugging in VBA
Now let’s introduce the debugging procedure for VBA scripts.
As an example, we’ll use the following sample code as a VBA script. Open the VBA editor and from the menu at the top left, go to VBA project > ThisWorkbook and open the workbook editor. (See image above)
Private Sub Workbook_Open()
' MsgBox "Workbook_Open"
Dim data As String
data = "hogehoge"
data = "fugafuga"
Dim dummy As Integer
dummy = 0
End SubCopy and paste the above code.
The above code can be executed/run with the F5 key. This code doesn’t make any major changes, and as you can see, it simply defines variables arbitrarily and exits.
The Workbook_Open() function writes programs that are automatically executed when a workbook is newly opened.
For example, if you uncomment ’ MsgBox “Workbook_Open” in the code above so it executes, a message box will be displayed the next time the above Excel file is opened.
As mentioned above, this program is also executed with the F5 key.
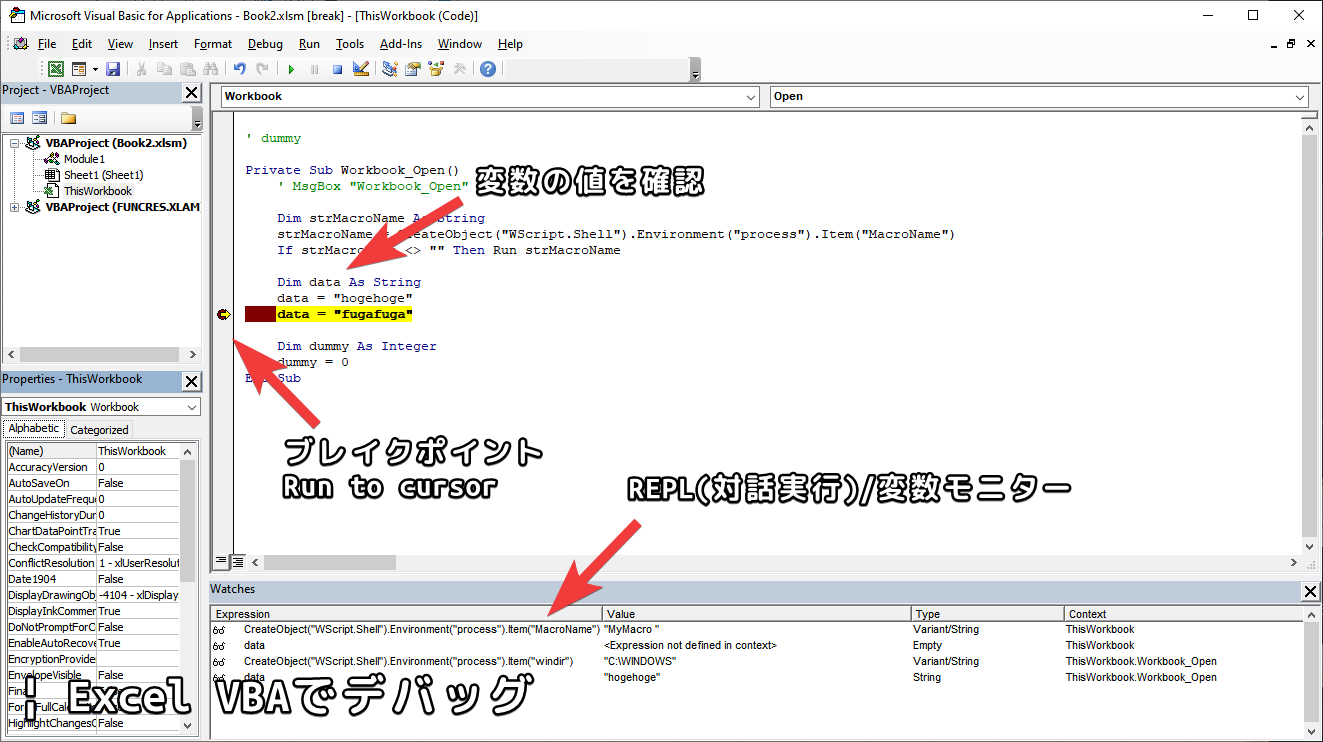
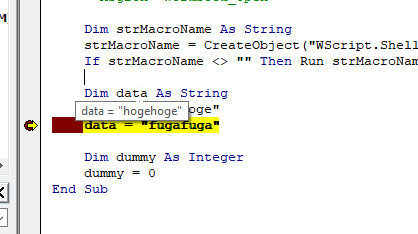
Breakpoint
By setting breakpoints, you can pause code execution at that point and check variable values or perform REPL (interactive execution) during that time. To set a breakpoint on any line, click the blank space on the left side of the line and confirm that the red circle icon is toggled. (See image above)
With the breakpoint set, press the F5 key to execute the script.
Run to cursor
With the program stopped at a breakpoint, when you continue execution, it will start from that line if you don’t do anything, but you can specify the line to continue from and release the break. This feature is called Run to cursor or Jump to cursor.
With Run to cursor, you can effectively create loops by returning the code to the top, or skip several lines at the bottom.
To specify the line to continue from with Run to cursor, focus on the right-pointing yellow arrow icon that appears to overlap with the red circle icon of the breakpoint. Drag this yellow arrow icon up or down with your mouse and set it to any line. Note that Run to cursor cannot be set on some code, such as Dim statements that define variables.
Checking Variables
With the program stopped at a breakpoint, you can check the value of any variable by hovering your mouse cursor over the variable.
Monitoring Variables and Program Expressions/Statements
From watches at the bottom of the screen, you can right-click and select add watch, or from Debug > add watch in the menu at the top of the screen, to monitor variables, expressions, and statement execution.
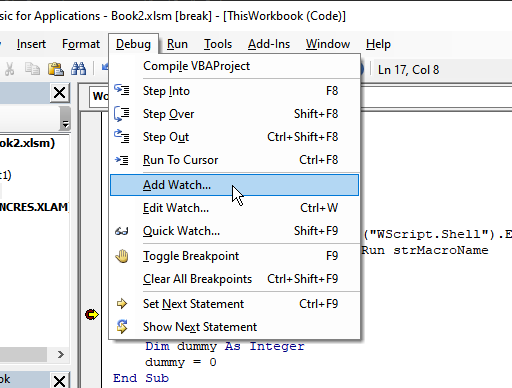
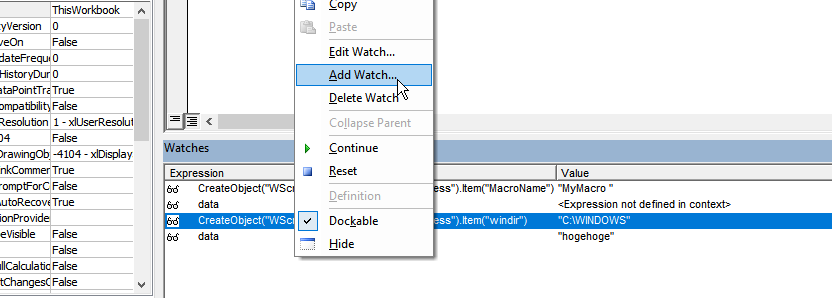
These list the values of set variables and program outputs when executed while the program is stopped at a breakpoint.
For example, in the image above, we’re stopped at a breakpoint at data = “hogehoge”, so “hogehoge” should be stored in the data variable.
Looking at the data column added to the watch, you can see it displays “hogehoge” as expected.
REPL (Interactive Execution)
REPL stands for interactive execution environment, referring to an environment where programs can be executed interactively.
For example, with the program stopped at a breakpoint in VBA, suppose you want to know what output the VBA program CreateObject(“WScript.Shell”).Environment(“process”).Item(“windir”) produces.
The point is that this can be executed line by line, like in the JavaScript console, which is essentially possible.
The specific method is to double-click any watch’s program/variable in watches to make it editable. If you enter any program here and complete the edit with the Enter key, etc., the program execution result will be output on the right side immediately.
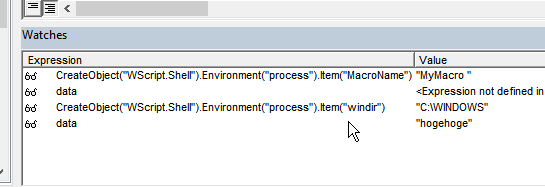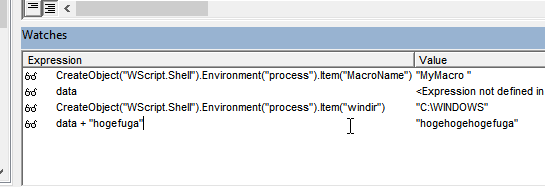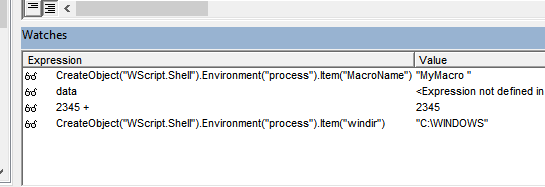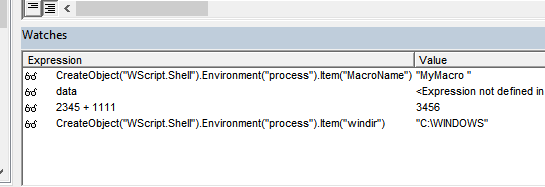
This doesn’t work completely for things like defining variables, assigning to variables, or complex expressions and blocks including control statements, and in this respect it differs from REPL debugging in VScode, but even considering that, it’s a highly valuable feature.
Summary
In this article, we introduced in detail how to debug programs using Excel VBA. Here’s a summary of the main points:
-
Enable Development Mode and VBA: To use the VBA editor in Excel, you need to enable development mode and the VBA editor. We explained the steps to enable the Developer tab.
-
Setting Breakpoints: By setting breakpoints, you can pause program execution. We set breakpoints on specific lines and paused code execution for detailed debugging.
-
Run to Cursor: After pausing at a breakpoint, we explained how to use Run to Cursor to move to a specific line and resume program execution.
-
Checking Variables: We introduced how to check variable values when the program is paused at a breakpoint. You can display the value of a variable by placing the cursor over it.
-
Variable Monitoring and Program Expression Monitoring: We explained how to monitor specific variables and program expression values using the watch feature. This allows you to track variable changes during program execution.
-
REPL (Interactive Execution): We introduced how to execute VBA programs in an interactive execution environment. We showed that you can interactively test parts of a program using this feature.
By utilizing these debugging techniques, you should be able to identify and fix errors in Excel VBA programs and proceed with efficient development.