This article explains how to install Ruby on Windows 11, configure it, and use it. We’ll install it using Chocolatey from PowerShell. Ruby is a language originating from Japan and is widely adopted in domestic programming education. It’s easy for beginners to learn due to the abundance of Japanese documentation and information, and it’s an active language with frameworks and libraries such as Ruby on Rails being actively developed.
In this article, we’ll install Ruby using Chocolatey.
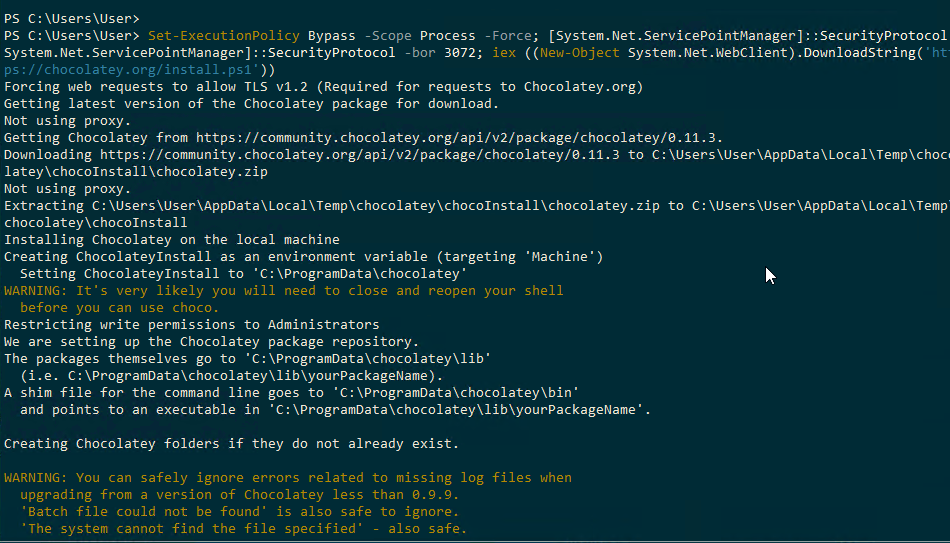
> Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol -bor 3072; iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://chocolatey.org/install.ps1'))If the following is displayed, the installation has completed successfully.
“Chocolatey (choco.exe) is now ready”
To ensure the installation was successful, check the version output.
> choco --version
0.11.3Run the refreshenv command.
> refreshenv
Refreshing environment variables from registry for cmd.exe. Please wait...Finished..At this point, various programming languages, development environments, libraries, and software available through Choco can be installed.
Now we’ll install Ruby using Choco.
Install Ruby with the following command.
> choco install ruby -y> choco install ruby -y
Chocolatey v0.11.3
Installing the following packages:
ruby
By installing, you accept licenses for the packages.
Progress: Downloading ruby 3.0.2.1... 100%
ruby v3.0.2.1 [Approved]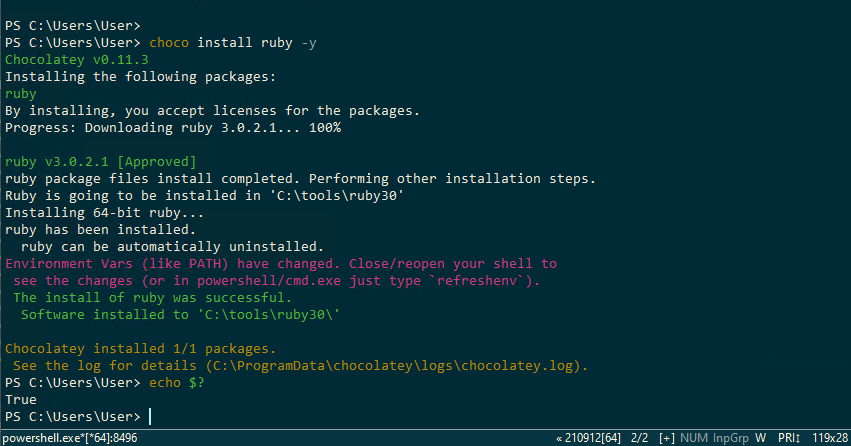
Ruby installation is complete at this point, but note that you must restart the console before the commands become available. For example, if you’re running powershell.exe, close that window and open a new one. If you’re using ConEmu, close ConEmu and open a new one. Alternatively, you can open a new instance without any issues.
If you run it in the same console window, you’ll get an error like this:
> ruby --version
ruby : The term 'ruby' is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable program.
Check the spelling of the name, or if a path was included, verify that the path is correct and try again.On a new console instance command line, check the Ruby version with the following command.
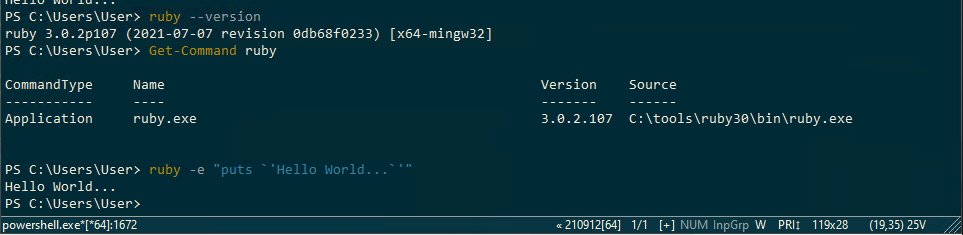
> ruby --version
ruby 3.0.2p107 (2021-07-07 revision 0db68f0233) [x64-mingw32]To check the installed folder and path, run the Get-Command command as follows. You can confirm it’s installed in the path (folder) C:\tools\ruby30\bin\ruby.exe.
> Get-Command ruby
CommandType Name Version Source
----------- ---- ------- ------
Application ruby.exe 3.0.2.107 C:\tools\ruby30\bin\ruby.exeLet’s try Hello World with Ruby.
> ruby -e "puts `'Hello World...`'"
Hello World...Note that the above command is for execution in PowerShell. It will probably error in WSL Bash or cmd.exe because the escape sequences are different. (Example below)
# ruby -e "puts `'Hello World...`'"
-e:1: syntax error, unexpected string literal, expecting end-of-input
puts `'Hello World...`'